As a new WordPress theme designer, you quickly learn the challenges of maintaining long CSS files while keeping them organized, scalable, and readable.
Many designers and front-end developers, including the ones here at WPBeginner, recommend using a CSS preprocessor language like Sass or LESS to make the job easier. But what are these preprocessors? And how do you get started with them?
This article is an introduction to Sass for new WordPress theme designers. We’ll tell you what a CSS preprocessor is, why you need it, and how to install and start using them right away.

What is Sass (Syntactically Awesome Stylesheet)?
The CSS that we use was designed to be an easy to use stylesheet language. However, web has evolved, and so designers need to have a stylesheet language that allows them to do more with less effort and time.
CSS preprocessor languages, like Sass, allow you to use features that are not currently available in the CSS such as variables, basic math operators, nesting, mixins, etc.
It is very much like PHP, which is a preprocessor language that executes a script on the server and generates an HTML output. Similarly, Sass preprocesses .scss files to generate CSS files that can be used by browsers.
Since version 3.8, WordPress admin area styles were ported to utilize Sass for development. There are many WordPress theme shops and developers already utilizing Sass to speed up their development process.
Getting Started With Sass for WordPress Theme Development
Most theme designers use local development environment to work on their themes before deploying it to a staging environment or a live server. Since Sass is a preprocessor language, you will need to install it on your local development environment.
The first thing you need to do is to install Sass. It can be used as a command line tool, but there are also some nice GUI Apps available for Sass. We recommend using Koala, which is a free opensource app available for Mac, Windows, and Linux.
For the sake of this article, you will need to create a blank theme. Simply create a new folder in /wp-content/themes/. You can name it ‘mytheme’ or anything else you want. Inside your blank theme folder create another folder and name it stylesheets.
In the stylesheets folder, you need to create a style.scss file using a text editor like Notepad.
Now you need to open Koala and click on the plus icon to add a new project. Next, locate your theme directory and add it as your project. You will notice that Koala will automatically find the Sass file in your stylesheets directory and display it.
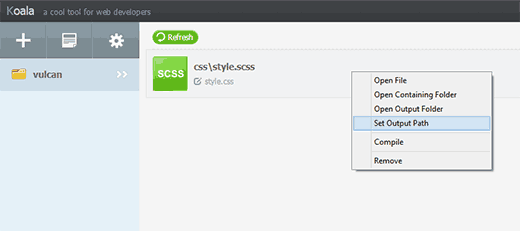
Right click on your Sass file and select Set Output Path option. Now select the root of your theme directory, example, /wp-content/themes/mytheme/ and hit enter. Koala will now generate CSS output file in your theme directory.
To test this you need to open your Sass file style.scss in a text editor like Notepad and add this code:
$fonts: arial, verdana, sans-serif;
body {
font-family:$fonts;
}
Now you need to save your changes and go back to Koala. Right click on your Sass file, and the sidebar will slide-in on the right. To compile your Sass file simply click on the ‘Compile’ button.
You can see the results by opening the style.css file in your theme directory, and it will have the processed CSS like this:
body {
font-family: arial, verdana, sans-serif; }
Notice that we have defined a variable $fonts in our Sass file. Now whenever we need to add font family we don’t need to type the names of all the fonts again. We can just use $fonts.
What Other Superpowers Sass Brings to CSS?
Sass is incredibly powerful, backward compatible, and super easy to learn. As we mentioned earlier that you can create variables, nesting, mixins, import, partials, mathematical and logical operators, etc.
Now we’ll show you some examples, and you can try them out on your WordPress theme.
Managing Multiple Stylesheets
One common problem that you will face as a WordPress theme designer is large stylesheets with a lot of sections. You will probably be scrolling up and down a lot to fix things while working on your theme.
Using Sass, you can import multiple files into your main stylesheet and output a single CSS file for your theme.
What about CSS @import?
The problem with using @import in your CSS file is that each time you add an @import, your CSS file makes another HTTP request to the server. This affects your page load time, which is not good for your project.
On the other hand, when you use @import in Sass, it will include the files in your Sass file and serve them all in a single CSS file for the browsers.
To learn how to use @import in Sass, first you need to create a reset.scss file in your theme’s stylesheets directory and paste this code in it.
/* http://meyerweb.com/eric/tools/css/reset/
v2.0 | 20110126
License: none (public domain)
*/
html, body, div, span, applet, object, iframe,
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p, blockquote, pre,
a, abbr, acronym, address, big, cite, code,
del, dfn, em, img, ins, kbd, q, s, samp,
small, strike, strong, sub, sup, tt, var,
b, u, i, center,
dl, dt, dd, ol, ul, li,
fieldset, form, label, legend,
table, caption, tbody, tfoot, thead, tr, th, td,
article, aside, canvas, details, embed,
figure, figcaption, footer, header, hgroup,
menu, nav, output, ruby, section, summary,
time, mark, audio, video {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: 0;
font-size: 100%;
font: inherit;
vertical-align: baseline;
}
/* HTML5 display-role reset for older browsers */
article, aside, details, figcaption, figure,
footer, header, hgroup, menu, nav, section {
display: block;
}
body {
line-height: 1;
}
ol, ul {
list-style: none;
}
blockquote, q {
quotes: none;
}
blockquote:before, blockquote:after,
q:before, q:after {
content: '';
content: none;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
Now you need to open your main style.scss file and add this line where you want the reset file to be imported:
@import 'reset';
Notice that you do not need to enter the full file name. To compile this, you need to open Koala and click the compile button again. Now open your theme’s main style.css file, and you will see your reset CSS included in it.
Nestin in Sass
Unlike HTML, CSS is not a nested language. Sass allows you to create nested files which are easy to manage and work with. For example, you can nest all elements for the <article> section, under the article selector.
As a WordPress theme designer, this allows you to work on different sections and style each element easily. To see nestin in action, add this to your style.scss file:
.entry-content {
p {
font-size:12px;
line-height:150%;
}
ul {
line-height:150%;
}
a:link, a:visited, a:active {
text-decoration:none;
color: #ff6633;
}
}
After processing, it will output the following CSS:
.entry-content p {
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 150%; }
.entry-content ul {
line-height: 150%; }
.entry-content a:link, .entry-content a:visited, .entry-content a:active {
text-decoration: none;
color: #ff6633; }
As a theme designer, you will be designing a different look and feel for widgets, posts, navigation menus, header, etc. Using nestin in Sass makes it well-structured, and you do not have to write the same classes, selectors and identifiers over and over again.
Using Mixins in Sass
Sometimes you would need to reuse some CSS throughout your project, even though the style rules will be the same because you will be using them on different selectors and classes. This is where mixins come in handy. Let’s add a mixin to your style.scss file:
@mixin hide-text{
overflow:hidden;
text-indent:-9000px;
display:block;
}
This mixin basically hides some text from being displayed. Here is an example of how you can use this mixin to hide text for your logo:
.logo{
background: url("logo.png");
height:100px;
width:200px;
@include hide-text;
}
Notice that you need to use @include to add a mixin. After processing, it will generate the following CSS:
.logo {
background: url("logo.png");
height: 100px;
width: 200px;
overflow: hidden;
text-indent: -9000px;
display: block; }
Mixins are also very helpful with vendor prefixes. When adding opacity values or border radius, using mixins you can save you a lot of time. Look at this example, where we have added a mixin to add border radius.
@mixin border-radius($radius) {
-webkit-border-radius: $radius;
-moz-border-radius: $radius;
-ms-border-radius: $radius;
-o-border-radius: $radius;
border-radius: $radius;
}
.largebutton { @include border-radius(10px); }
.smallbutton { @include border-radius(5px); }
After compiling, it will generate the following CSS:
.largebutton {
-webkit-border-radius: 10px;
-moz-border-radius: 10px;
-ms-border-radius: 10px;
-o-border-radius: 10px;
border-radius: 10px; }
.smallbutton {
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
-ms-border-radius: 5px;
-o-border-radius: 5px;
border-radius: 5px; }
Additional Resources
We hope that this article helped you learn about Sass for WordPress theme development. Many WordPress theme designers are already using it. Some go as far as to say that in future all CSS will be preprocessed, and WordPress theme developers need to up their game. You may also want to see our guide on WordPress body class tips for theme designers, or our expert picks of the best drag and drop WordPress page builders.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.





Dennis Muthomi
Thanks for this Sass for WordPress theme designers guide. As a newb, I found the nesting section super helpful. Who knew code could get so clean and organized?
I’ve been playing with Sass in my own projects and I’ve found using partials for different parts of my theme (header, footer, sidebar) has really streamlined my workflow.
This has motivated me to dive into mixins to further simplify my CSS.
Great resource btw
Dapo O
Thanks for this.
I’m building a custom Block theme and wondering if I can use SASS same way I do with Classic themes.
WPBeginner Support
There are some differences in how CSS is added with a Block theme compared to Classic themes.
Admin
Mark
Great tutorial. How do you go about creating a Wordpress child theme using SASS and Koala? That would be a very useful tutorial…
WPBeginner Support
While we don’t have a guide for that at the moment, we will certainly take a look at it for a possible article.
Admin
Paulo Jesus
Hi, I am working on a WordPress theme using bootstrap and sass. I have a sass folder set up using the smacss aproach and on the root of my sass folder I have a style.sccs file that imports all the scss files for all the sections on my theme(_footer.scss, _header.scss, etc) then it outputs to my style.css file on the root of my theme. The issue I am having is that I am extending some bootstrap classes in some of those .scss files and if I include a _bootstrap.scss on my sass folder and import it on my style.scss file everything works fine, however the whole bootstrap is then also compiled to my style.css and it becomes quite messy. Ideally I would want the bootstrap css separated from my them styles not as part of my style.css, however if I dont import it on my style.scss and instead enqueue it on my functions.php I get an error saying that the bootstrap classes extended cannot be found and the theme breaks.. Any thoughts on how to go around this issue would be appreciated.
Thank you very much
Cinnamon Bernard
Hi,
I know this is sort of an old post, but still quite new, I had a question about incorporating Twitter Bootstrap Sass, Font-Awesome Sass, with Underscores Wordpress starter theme template.
I’ve tried to incorporate and placed all Sass files in their own directory, and have a separate output path for Css files, while keeping Wordpress style.css in the root with an @import to the style.css within the Css folder.
After setting all of this up, the styles for bootstrap has not been working properly, I’m not certain if it is due to having a reset file. I was sure to place the bootstrap and font-awesome @imports at the top, followed by the others.
If possible, based on what I’ve provided, can you give advice on how to set up my workflow.
Thanks!
Rehan
Awesome tutorial
Thanks
Ricardo Gutierrez
Hello.
Is the “reset” better than normalize ?
Thnks !
WPBeginner Support
Reset would unset browser styles, while normalize uses a consistent style across browser. We think each developer would have their own preference. We would prefer to work with reset.
Admin
Josh McClanahan
Great article!
I was wondering if there is any kind of setup, like in php you have to add PEAR for various extensions, for using SASS especially when going live.
In other words is there anything that is needed to be included after compiling and going live?
Thanks for your help and this article.
WPBeginner Support
No Josh, after compiling it generates the regular CSS output.
Admin